
Brain waves and their importance for sleep
Alpha, Theta, Delta – different activities can be observed in our brain during sleep. Brain waves also change depending on the sleep phase. Learn more about the significance of the different brain frequencies and which brain waves occur particularly during sleep here.
Table of contents:
- How do brain waves arise?
- What brain waves are there?
- What role do brain waves play in sleep?
- Can brain waves be influenced?
- Conclusion
1. How do brain waves arise?
The human brain consists of approximately 80 billion nerve cells, called neurons, which connect and communicate with each other using electrical impulses. Each of these impulses generates tiny electromagnetic waves with a frequency of up to 100 oscillations per second (100 hertz). The numerous different waves overlap and form an electromagnetic pattern that can be measured using electroencephalography (EEG). Special electrodes are attached to the scalp to record the electrical activity.
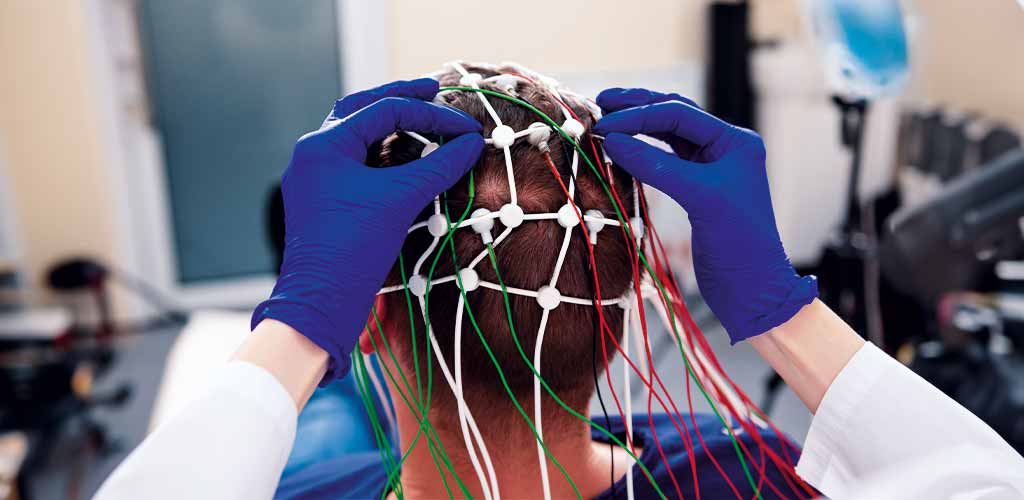
The different brain waves can be linked to specific states of consciousness and activities. The more intensely the brain is working, the stronger the impulses and vibrations of the nerve cells. Which brain waves predominate at a given moment can therefore provide information about brain activity and indicate the current state of our brain and consciousness.
2. What brain waves are there?
As a rule, 5 types of brain waves are distinguished based on their vibration spectrum: gamma, beta, alpha, theta and delta waves.
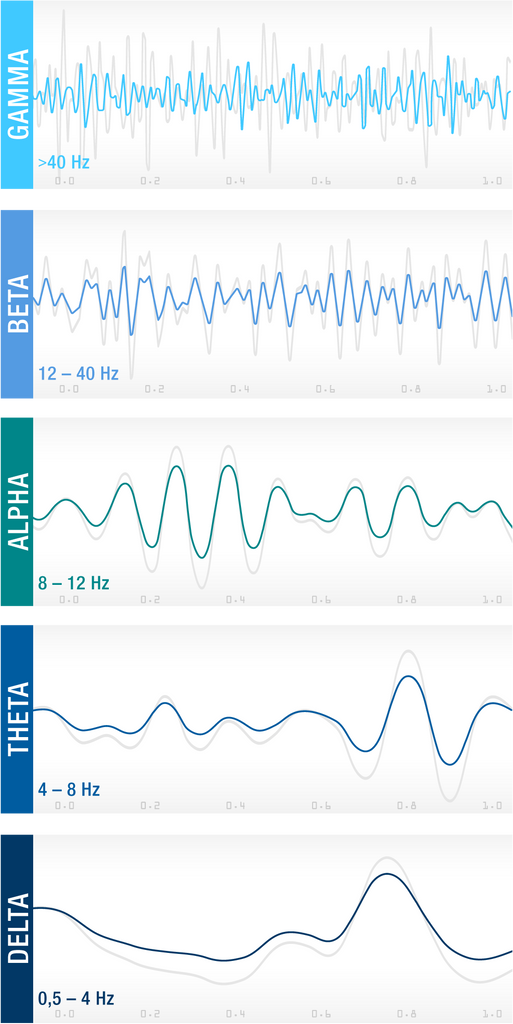
Gamma (approx. 40-100 Hz)
Gamma waves are very fast brain waves that enable rapid information transfer from one brain area to another. They occur exclusively in the waking state and are more pronounced when we perform demanding tasks that require high levels of concentration and performance. Gamma waves have been little researched, but scientists now suspect that they are also related to the coordination of cell networks in the brain.
Beta (12 – 40 Hz)
Beta waves can be measured when we are in an alert, waking state and are therefore the brain waves that predominate during the day in a normal, healthy person. They indicate a state in which we are fully conscious, receptive, and focused.
Low beta frequencies represent a relaxed but alert state. The middle beta range corresponds to a healthy waking state with normal performance. A high beta wave range, on the other hand, indicates an increased release of stress hormones and can reflect anxiety, stress or nervousness.
Alpha (8 – 12 Hz)
Alpha waves are somewhat slower than beta waves. They usually occur when we transition from the waking to the resting state and form a bridge between the conscious and subconscious. While we are awake, we are very passive and relaxed. Our concentration and ability to absorb information is reduced, and we are in a kind of standby state that can also lead to sleep. Alpha waves are associated with a high ability to learn and remember, which can actually also be evident during the transition in or out of sleep. Those who transition from the theta range (sleep) to a semi-sleep (alpha range) upon waking in the morning are highly likely to be able to remember their Dreams remember.If, on the other hand, we switch directly to the beta state, we can no longer remember what we dreamed.
Theta (4 – 8 Hz)
When we slowly transition from waking to sleep, theta waves are predominantly seen in the EEG. They arise in a state in which the conscious mind withdraws and the subconscious becomes increasingly active. Theta waves are therefore usually found when falling asleep, in the light Sleep phases, dream sleep (REM sleep), but also in deep meditation or hypnotic trance. Special features of this phase are a pronounced fantasy, a high level of vivid imagination and the loss of conscious thought function, which is typical for the Dream phases of sleep.
Delta (0.5 – 4 Hz)
Slow delta waves occur primarily during deep sleep and are rarely seen during waking hours. During these phases, we sleep soundly because our consciousness is completely suspended. The body, instead, focuses on regenerative and healing processes; growth hormones are released, and the health of all cells and organs is ensured. For this reason, deep sleep is considered one of the body's most important recovery periods, one we never consciously experience but desperately need.
3. What role do brain waves play in sleep?
Every night we go through several sleep cycles, which are divided into four Sleep phases In each of these sleep phases, something different happens in our brain – the Memory is formed, memory is linked, or the energy stores in the body's cells are replenished. Due to these different activities, very specific brain waves appear in the individual sleep phases.
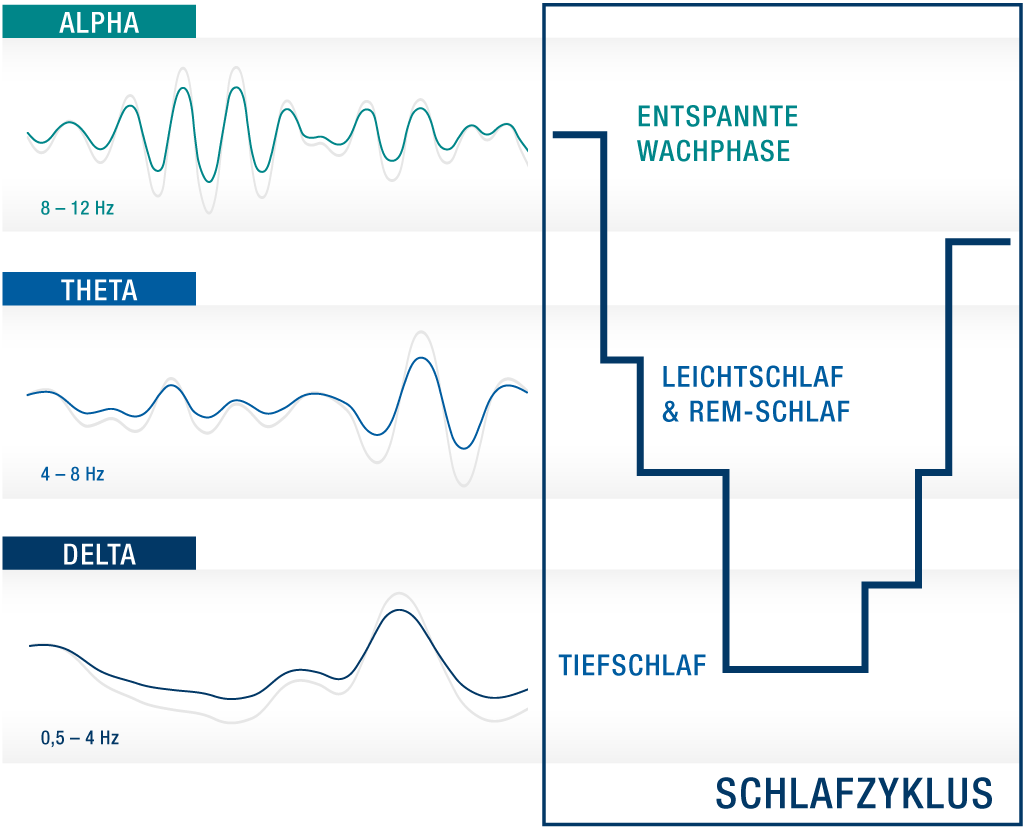
When we sleep, we calm down and conscious activity slows down. Therefore, sleep is primarily associated with the slower theta and delta brain waves.
Before going to bed Ideally, we begin to relax and reduce our activity. Beta waves slow down to alpha waves, and we enter a calm, perhaps even sleepy state. When falling asleep the alpha waves usually change into slow theta waves, consciousness fades and we slip into light sleep. Transition to deep sleep phase we are then in the delta wave area. In the following REM sleep brain activity increases again, we dream and primarily theta waves are created.
Brain activity is also strongly linked to energy metabolism. Since almost every neuronal impulse requires energy, energy consumption is significantly higher during periods of high activity (gamma, beta) than during periods of reduced activity. During deep sleep (delta waves), energy consumption in the brain is 40% lower than during wakefulness. This is also the reason why (Deep) sleep allows us to replenish our energy reserves and start the next day full of energy, literally.
 Awakening from sleep can lead to the beta waves typical of the waking state via alpha waves, or it can transition directly from the unconscious theta state to the beta range. However, those who skip the half-sleep state are less likely to remember their dreams than those for whom alpha waves serve as a bridge back to consciousness.
Awakening from sleep can lead to the beta waves typical of the waking state via alpha waves, or it can transition directly from the unconscious theta state to the beta range. However, those who skip the half-sleep state are less likely to remember their dreams than those for whom alpha waves serve as a bridge back to consciousness.
Measuring brain waves plays a major role in sleep research because it can provide information about when we are in which sleep phase.The EEG is therefore an integral part of the so-called polysomnography (PSG), which is considered the gold standard in sleep medicine for the diagnosis of Sleep disorders applies.
4. Can brain waves be influenced?
The human brain is characterized by a high degree of adaptability, also known as plasticity. This allows it to adapt its activity to external influences if these dictate a certain rhythm. This can be particularly helpful in diseases such as Parkinson's or Alzheimer's, which are associated with altered brain activity.
To a certain extent, we can also learn to change our brain waves ourselves by controlling our state of consciousness, for example, through meditation or hypnosis. However, this doesn't work in all wavebands. Brain waves can be best influenced in the beta and alpha frequency ranges, i.e., in the active and passive waking states.
Ways to influence brain waves:
- Meditation/Hypnosis
- Acoustic signals (e.g. binaural rhythms, Sounds with certain frequencies)
- Visual stimuli (e.g. strobe light therapy)
- Neurofeedback
- Electromagnetic stimulation (e.g. transcranial magnetic stimulation)
5. Conclusion
-
Brain waves are created by electrical impulses in the brain and are related to the state of consciousness and activity
-
There are 5 types of waves based on frequency: Gamma, Beta, Alpha, Theta and Delta
-
During sleep, theta (light sleep, REM sleep) and delta waves (deep sleep) occur primarily
-
Brain waves can be partially influenced, for example through meditation, hypnosis, acoustic and visual stimuli or special neurofeedback and stimulation therapies
Best wishes and see you soon!



Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.