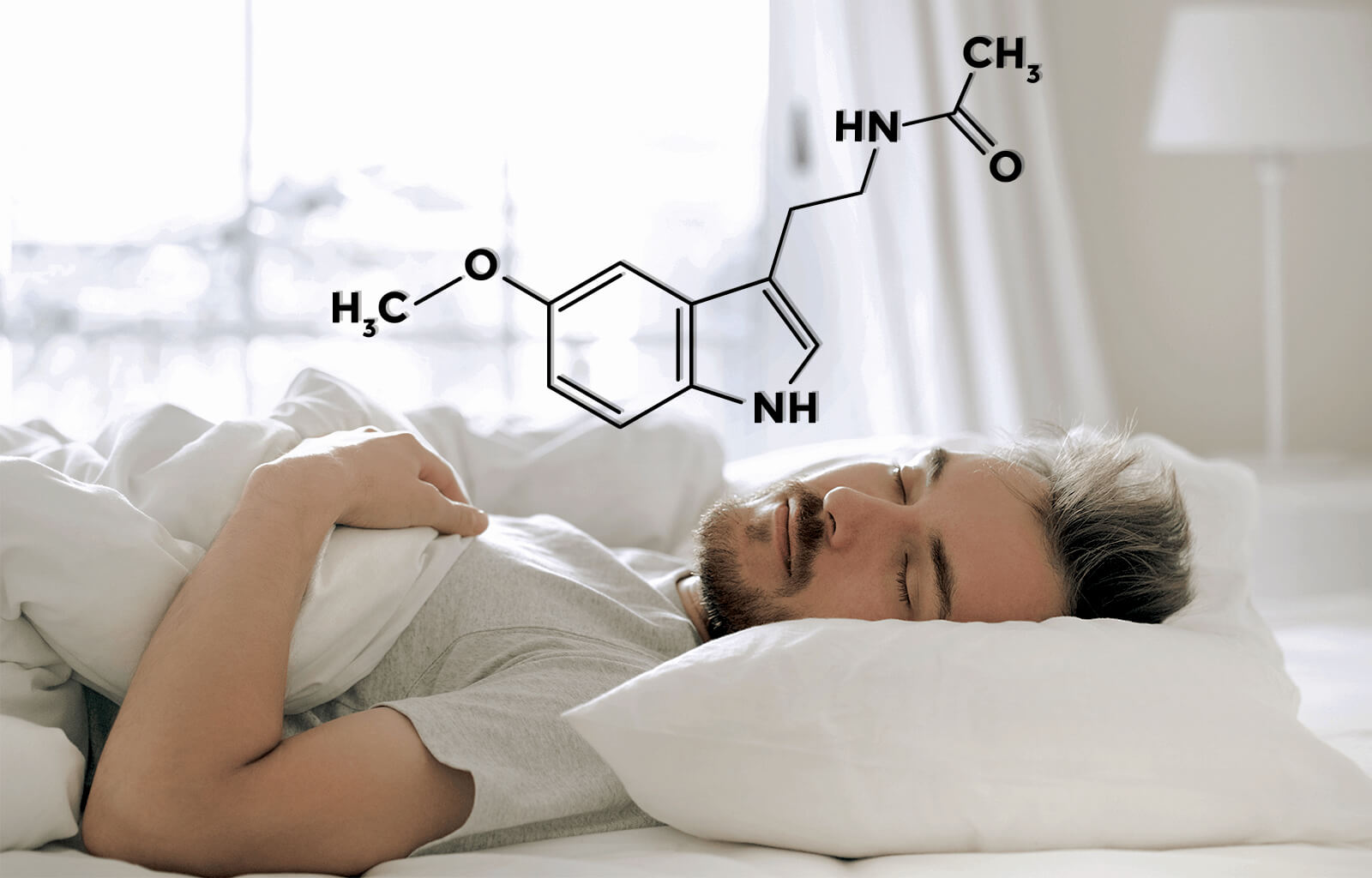
The sleep hormone melatonin
Melatonin is considered a miracle cure for sleep disorders. This sleep hormone plays a central role in our body, regulating our sleep-wake cycle and also influencing our health and well-being. But what is melatonin, and what does it do? You can find an overview of the importance, tasks, and functions of melatonin here.
Table of contents
- What is melatonin?
- How melatonin is produced
- Consequences of a disturbed melatonin balance
- Melatonin as a dietary supplement
- Melatonin – The basis of good sleep
1. What is melatonin?
Melatonin is one of our body's own hormones, produced in the brain and classified as a neurotransmitter. These are messenger substances that act as communication points in all nerve cells throughout the body, transporting important information and thus regulating metabolic processes in our body. A balanced hormone balance is therefore very important for the healthy functioning of our body.

The hormone melatonin plays a key role in regulating our sleep-wake cycle and is therefore also called the "sleep hormone." In interaction with cortisol, known as the "stress hormone," it regulates our circadian rhythm. Towards evening, the concentration of melatonin in the body increases, causing us to become tired, calm down, and fall asleep. Therefore, to fall asleep without difficulty, our body must produce sufficient amounts of melatonin and have enough time to relax. You can find tips for relaxing before bed in this Article. In addition to this important function for sleep and nighttime regeneration, which are essential for our health, melatonin also influences our psyche and also has a strong antioxidant effect, which helps prevent cell damage.
2. How melatonin is produced

The conversion of the neurotransmitter serotonin into melatonin is one of the main functions of the pineal gland (epiphysis), located in the center of our brain. Its function is significantly influenced by light and darkness, and thus also by the natural day-night rhythm. During the day, the body produces serotonin, known as the happiness hormone due to its relaxing and mood-enhancing effects. As darkness falls, the conversion of serotonin into the sleep hormone melatonin begins. Between 2 and 4 a.m., the melatonin concentration in our blood is highest – before it decreases again and is suppressed by the approaching daylight.
3. Consequences of a disturbed melatonin balance
The disruption of the body's own melatonin production can ultimately lead to sleep disturbances or difficulty falling asleep. If this important conversion is inhibited in the evening by unnatural light conditions, the body cannot produce enough melatonin and thus lacks clear signals to prepare for sleep. This happens easily these days, as we illuminate our rooms with artificial light sources, contrary to natural darkness, or use screens such as televisions and
By the way: Due to the usually few hours of daylight, the melatonin level in the blood remains elevated even during the day, especially in winter. This is what causes the intense fatigue and listlessness experienced during the cold season. Here you will learn how to stay fit through autumn and winter.
4. Melatonin as a dietary supplement

Today, there are already numerous medications and supplements that supply the body with melatonin, thus promoting sleep and improving our sleep patterns. There are two ways to support the body naturally.
Direct support: Melatonin
Melatonin can be absorbed directly into our bodies, for example, in capsule form or as a mouth spray. Studies show that supplemental intake of the sleep hormone actually helps us fall asleep faster. The recommended dose is 1 to 2 mg of melatonin per day, taken some time before bedtime, depending on the dosage form. This can naturally support fatigue and sleepiness by increasing melatonin levels and allowing the body to receive the important signals for sleep.
Indirect support: L-tryptophan
The happiness hormone serotonin is converted into melatonin in the dark. Therefore, a healthy serotonin level is not only beneficial for our mood and well-being, but also an important prerequisite for melatonin production.
L-tryptophan is an essential amino acid and a basic building block of serotonin. Taking L-tryptophan supplements helps provide the body with an important building block so it can naturally produce sufficient serotonin and, in the next step, melatonin.
5. Melatonin – The basis of good sleep

As you can see, melatonin, known as the sleep hormone, is an essential neurotransmitter that plays a truly central role in our health. To fall asleep easily and support healthy sleep habits, we should pay attention to our melatonin levels and ensure that our bodies can naturally produce sufficient sleep hormones.
Our tip: Dim the lights a few hours before bedtime and try to avoid bright screens and other light sources in the evening, especially at night. You can also make sure you eat a balanced diet and get enough daylight during the day. This will provide your body with sufficient L-tryptophan, promote light-induced serotonin production, and optimally prepare it for evening melatonin synthesis.
6. Conclusion
-
The sleep hormone melatonin is a messenger substance produced by the body that regulates the sleep-wake rhythm and makes us tired and sleepy in the evening.
-
When darkness increases or light is lacking, the happiness hormone serotonin is converted into melatonin in the brain
-
Low melatonin levels promote sleep disorders and difficulty falling asleep.
-
Dietary supplements containing melatonin are well tolerated and can help you fall asleep.
-
L-tryptophan is a basic building block of serotonin and can positively influence melatonin production.
-
Support your sleep by getting daylight during the day to produce serotonin, eating a balanced diet to supply your body with L-tryptophan, and dimming the lights in the evening.
Best wishes and see you soon!



Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.