
Our skin in sleep
During the day, our skin protects our body from harmful environmental influences and determines our external appearance. At night, it regenerates. Therefore, lack of sleep not only harms our health—it also unfortunately shows. Here, you'll learn exactly what happens to our skin during sleep and why restful sleep is crucial for healthy and beautiful skin.
Table of contents
- Our skin
- Onstructure & function of the skin
- Skin & Sleep
- Lack of sleep damages the skin
- How the skin regenerates during sleep
- Support for skin health & beauty sleep
- Conclusion
1. Our skin
The skin is one of the most important organs in our body and forms the basis for a well-groomed external appearance. It covers the entire surface of our body, is one of our sensory organs, and represents a vital protective barrier that protects the body from numerous harmful influences. During the day, our skin is particularly vulnerable to the effects of light and UV radiation, heat, cold, injuries, and infections. Depending on the time of day, the moisture content, pH value, temperature, and activity of the sebaceous and sweat glands fluctuate. At night, when we rest and sleep, numerous important regenerative processes take place in our body, and our skin also recovers from the harmful influences it is exposed to in everyday life. Adequate and restful sleep is therefore of great importance for maintaining and caring for healthy and strong skin.
2. Structure & function of the skin
The skin is composed of three different layers. Each of these layers fulfills different functions that are crucial to our health, not only externally but also internally.
1 - Epidermis (top layer of skin)
The epidermis consists largely of a stratum corneum and forms the skin's outermost protective barrier. It is primarily responsible for defending against harmful substances and pathogens and also provides mechanical protection against impacts, cuts, and blows.
2 - Dermis (leather skin)
The dermis, located beneath the epidermis, consists of collagen-containing connective tissue fibers that provide elasticity and firmness. The dermis also contains numerous blood and lymph vessels, sebaceous and sweat glands, as well as numerous nerve fibers, blood vessels, and muscle cells.
3 - Subcutaneous tissue
The last layer of skin is made up of loose connective and fatty tissue and separates the skin from other tissue inside the body.

The different layers of skin perform numerous different functions. These include, for example, protection from toxins and harmful radiation or the defense against pathogens through the important protective acid mantle. The skin also plays an important role in regulating our Body temperatureIt protects the body from dehydration and extreme stress caused by extreme heat or cold, and as a sensory organ, it is capable of sensing a wide variety of stimuli (e.g., temperature, pain, pressure). The skin also performs important functions internally. It contains important immune cells, produces vitamin D, which is essential for the body, and serves, among other things, to store water, fat, and various metabolic products.
In addition to these crucial functions for our health, our skin also plays a key role in our outward appearance. Our skin's appearance therefore quickly reveals when we are ill or our body is lacking nutrients. A smooth, even complexion is also considered attractive, which is why our appearance and beauty also benefit from healthy skin.
3. Lack of sleep damages the skin
At night, our body breaks down harmful substances and restores the skin's natural protective barriers, maintains firmness and elasticity, and regulates moisture levels. Important growth hormones are released, which are involved in almost all functions in our body, help build connective tissue, and regulate enzyme production and cell renewal. lack of sleep disrupts these natural recovery processes and slows down the skin's own repair mechanisms. If we don't get enough sleep, the body releases more of what is known as "stress hormone", which puts the body into a state of stress. Excessively high cortisol levels promote inflammation in the tissue structures, increase the activity of the sebaceous glands, and inhibit the body's production of hyaluronic acid. This leads to redness, inflammation, and increased wrinkle formation. The skin also loses firmness and moisture, becomes dry and cracked, and appears visibly aged. Furthermore, cortisol damages the skin's barrier function and, especially in the long term, leads to an increase in blood sugar, which then hardens the collagen structures and reduces the skin's elasticity.

lack of sleep This causes immense damage to our skin and leaves visible short- and long-term consequences. Our skin loses tone, elasticity, and moisture. This leads to dark circles under the eyes or a pale complexion the following day, a reduced function of the immune and protective barrier, and increased susceptibility to injury. Restful sleep, on the other hand, helps maintain healthy skin and also counteracts the natural signs of aging.
4. How the skin regenerates during sleep
Metabolism and cell renewal
At night, and especially during deep sleep phases, growth hormones are released in increased amounts, and the body's own collagen production also operates at full speed. This promotes cell renewal in muscles and connective tissue, breaks down old cells, repairs damaged cells, removes harmful substances and waste products, and builds new cells. At night, our skin also receives better blood circulation, improving metabolism, supplying skin cells with nutrients and oxygen more effectively, and accelerating the removal of harmful substances.
New studies also assume that the Sleep hormone melatonin can have a positive effect on our skin. Melatonin functions as an antioxidant and is thus able to neutralize free radicals within the body and protect cells from damage caused by these aggressive substances and stress. It also has a positive effect on collagen production and can help protect the skin from UV radiation and the resulting damage, such as wrinkles or dark spots.
Fat and moisture content
During the day, the skin is exposed to numerous environmental influences, so the moisture content, pH value, temperature, and activity of the sebaceous and sweat glands located in the middle layer of the skin fluctuate depending on the time of day and stress. At night, these stresses are absent, and sebaceous gland activity decreases.This removes deposits in the skin pores, regulates the skin's oil content and replenishes moisture reserves.
Tension and elasticity
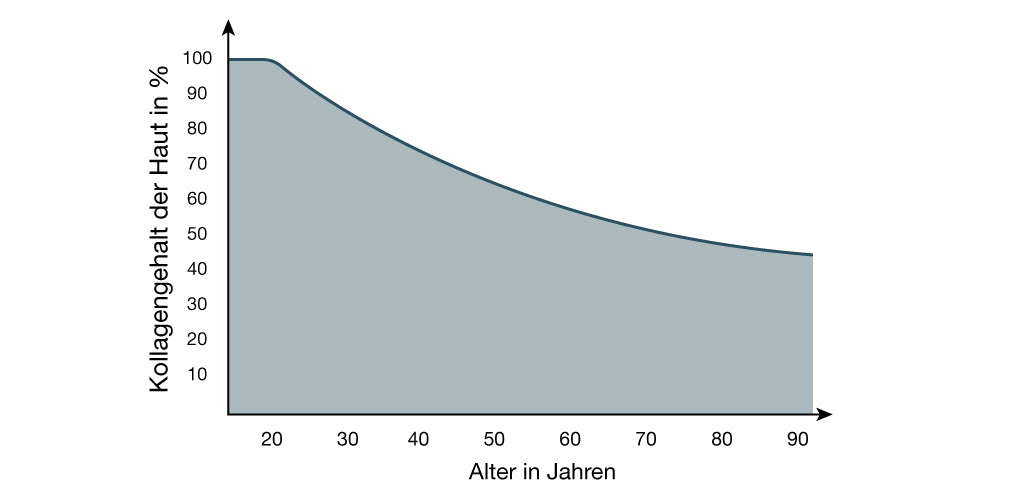
The body's own substances collagen and hyaluronic acid play an important role in the firmness and elasticity of our skin. Our skin is composed of 80% of the structural protein collagen, whose fibers support the skin's layers and ensure firmness. Hyaluronic acid is a key component of connective tissue and is responsible for a firm skin appearance and skin moisture content. Especially during sleep, the production of these important building blocks runs at full speed, thus maintaining our skin's firmness and elasticity. This prevents the formation of wrinkles and fine lines and promotes a healthy and firm complexion.
5. Support for skin health & beauty sleep

To support skin regeneration overnight, you should ensure you get enough sleep, but also the highest possible quality. It is during deep sleep, in particular, that essential growth hormones are released and the most important repair processes take place. Learn more here more about the individual sleep phases or read our tips for a healthy Sleep behavior. Before going to bed, proper care and sufficient nutrient supply are essential to ensure that the skin is free of impurities and that the body has sufficient material available for cell repair and renewal. You can find the most important and effective tips for optimally preparing your skin for sleep in this article.
More about the perfect evening routine and the ideal beauty sleep:
5 ultimate tips for your beauty sleep
Why good sleep makes you beautiful
6. Conclusion
-
The skin consists of three layers (epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous tissue) and protects the body from harmful environmental influences such as UV radiation, heat, injuries or infections.
-
Lack of sleep damages the skin, reduces its barrier capacity and impairs a healthy, beautiful complexion.
-
During sleep, the skin recovers and numerous regeneration processes ensure cell repair and renewal, the regulation of fat and moisture content and the maintenance of firmness and elasticity.
Best wishes and see you soon!



Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.